Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yogo, Akifumi; Inoue, Norihiro*; Sakaki, Hironao; Fukuda, Yuji; Jinno, Satoshi; Kanasaki, Masato; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Shimomura, Takuya; Ogura, Koichi; Mori, Michiaki; et al.
no journal, ,
The laser-ion acceleration can be complicated by the presence of an amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) pedestal at a leading edge of the high-intensity laser pulse. Several attempts have been made to decrease the ASE level by using a plasma mirror or a OPCPA laser system combined with a saturable absorber: J-KAREN. In this work, we propose another way to improve the main pulse-ASE ratio by using a double-CPA bypass line system. We have developed a new laser line consisting of a pulse compressor, a saturable absorber, a pulse stretcher and a Ti:Sap. multi-pass amplifier. The most remarkable feature of this system is that the bypass line can be installed into a conventional TW laser system.
Kotaki, Hideyuki; Hayashi, Yukio; Mori, Michiaki; Kando, Masaki; Koga, J. K.; Bulanov, S. V.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tsubouchi, Masaaki; Nagai, Masaya*; Oshima, Yasuhiro*
no journal, ,
We have proposed a novel technique for the THz tomography of photo-induced carriers based on optical-pump THz-probe reflection spectroscopy with the counter-propagated pump and probe pulses. We have experimentally demonstrated it with silicon. The obtained complex reflection can be reproduced by the exact solution of Maxwell's equations.
Oka, Kiyoshi; Seki, Takeshi; Akatsu, Tomohiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nishikino, Masaharu; Hasegawa, Noboru; Tomita, Takuro*; Takei, Ryota*; Baba, Motoyoshi*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Yamagiwa, Mitsuru; Suemoto, Toru
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Mori, Michiaki; Shimomura, Takuya; Tanoue, Manabu; Kondo, Shuji; Kanazawa, Shuhei; Daito, Izuru; Suzuki, Masayuki*; Okada, Hajime; Ochi, Yoshihiro; et al.
no journal, ,
We describe two specific high intensity laser systems that are being developed in our laboratory for many applications such as high field science, nonlinear optics. We report on an ultra-high intensity petawatt-class Ti:sapphire chirped-pulse amplification laser system that can produce a pulse energy of  18 J with
18 J with  30 fs pulse duration for studying extremely high intensity laser matter interaction process and a small-scaled Yb:YAG chirped-pulse amplification laser system that can generate a pulse energy of
30 fs pulse duration for studying extremely high intensity laser matter interaction process and a small-scaled Yb:YAG chirped-pulse amplification laser system that can generate a pulse energy of  100 m J of
100 m J of  500 fs pulse duration for compact, high efficiency, high repetition system. We discuss the basic design aspects and present the results from our experimental investigations of these laser systems.
500 fs pulse duration for compact, high efficiency, high repetition system. We discuss the basic design aspects and present the results from our experimental investigations of these laser systems.
Akagi, Hiroshi; Kasajima, Tatsuya*; Kumada, Takayuki; Itakura, Ryuji; Yokoyama, Atsushi; Hasegawa, Hirokazu*; Oshima, Yasuhiro*
no journal, ,
We demonstrate the isotope selection with molecular alignment and angle-dependent ionization in intense laser fields. The 14-N2 and 15-N2 mixed gas is irradiated with a linearly polarized femtosecond laser pulse for creation of rotational wavepackets. After a certain delay when one of two isotopologues is aligned along the laser polarization direction, another linearly polarized femtosecond laser pulse is shined for ionization. It is confirmed that the ionization yield ratio between the two isotopologues can be changed as a function of the delay between the two laser pulses.
Itakura, Ryuji; Ikuta, Tomoya*; Hosaka, Koichi*; Akagi, Hiroshi; Yokoyama, Atsushi; Yamanouchi, Kaoru*; Kannari, Fumihiko*
no journal, ,
We investigate dissociative ionization of ethanol induced by intense laser fields using photoelectron-photo ion coincidence momentum imaging. Our attention is focused on the correlation between (1) photoelectron energy reflecting the state of ethanol cation at ionization and (2) kinetic energy of a fragment ion. From the observed correlation maps, we clarified that the internal energy gained from the laser field strongly depends on the ionization and dissociation pathways.
Terada, Takaya; Ito, Fuyumi; Nishimura, Akihiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kanasaki, Masato; Fukuda, Yuji; Sakaki, Hironao; Yogo, Akifumi; Jinno, Satoshi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Hattori, Atsuto*; Matsukawa, Kenya*; Kondo, Kiminori; Oda, Keiji*; et al.
no journal, ,
In laser-driven ion acceleration experiments applying cluster-gas target, along with high energy ions, a significant amount of well-collimated high energy electrons with several hundreds of MeV are produced. Such fast electrons could produce high energy photons via bremsstrahlung processes. Furthermore, such photons could produce photo-neutrons in a series of ( ,n) reactions. If CR-39 detectors, which can detect only ions and it is insensitive to high energy photons and electrons, is exposed to such photo-neutrons, it can record recoiled protons and other heavy ions generated by the nuclear reactions. In order to precisely diagnose only for laser accelerated ions, we have to keep the photo-neutron flux level as low as possible, because it could cause significant contaminant effects to the CR-39 as a background noise. In the present study, to minimize the flux of photo-neutrons, we have considered the geometry of the stacked CR-39 detector unit by using Monte Carlo simulation.
,n) reactions. If CR-39 detectors, which can detect only ions and it is insensitive to high energy photons and electrons, is exposed to such photo-neutrons, it can record recoiled protons and other heavy ions generated by the nuclear reactions. In order to precisely diagnose only for laser accelerated ions, we have to keep the photo-neutron flux level as low as possible, because it could cause significant contaminant effects to the CR-39 as a background noise. In the present study, to minimize the flux of photo-neutrons, we have considered the geometry of the stacked CR-39 detector unit by using Monte Carlo simulation.
 :(GSAG
:(GSAG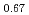 :YSGG
:YSGG ) laser
) laserKosuge, Atsushi; Okada, Hajime; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Nagashima, Keisuke; Yanagitani, Takagimi*; Yagi, Hideki*; Meichin, Noriyuki*
no journal, ,
One of the common high power pulsed lasers are based on a Nd-doped laser, but the pulses are not short of femtosecond region. Recently, the development of a new ceramic laser medium has been reported, namely the Nd-doped mixed scandium garnets Nd :(GSAG
:(GSAG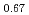 :YSGG
:YSGG ). The Nd
). The Nd : (GSAG
: (GSAG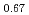 :YSGG
:YSGG ) has a significantly broader spectral bandwidth (5 nm) and four times higher thermal conductivity than Nd-doped glass materials. And the ceramics have a potential for a high power laser system because they have a size scalability and stronger fracture toughness than single crystal. We successfully demonstrated for the first time a mode-locked Nd
) has a significantly broader spectral bandwidth (5 nm) and four times higher thermal conductivity than Nd-doped glass materials. And the ceramics have a potential for a high power laser system because they have a size scalability and stronger fracture toughness than single crystal. We successfully demonstrated for the first time a mode-locked Nd -doped mixed scandium garnets (Nd
-doped mixed scandium garnets (Nd :(GSAG
:(GSAG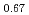 :YSGG
:YSGG )) ceramic laser.
)) ceramic laser.
Jinno, Satoshi; Fukuda, Yuji; Sakaki, Hironao; Yogo, Akifumi; Kanasaki, Masato; Kondo, Kiminori; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Pikuz, T.; Boldarev, A. S.*; et al.
no journal, ,
We have achieved high-energy ion generation in the laser driven ion acceleration using cluster-gas targets, which has been prepared by using the nozzle specially designed based on the Boldarev's model. However, a characterization of the cluster-gas targets is not sufficient to further investigate the ion acceleration mechanism and optimize the acceleration condition. In present work, the target diagnosis apparatus applying Mie scattering and interferometry has been developed. The sub-micron sized CO clusters were verified by measuring the angular distribution of the scattering light from the mixed gas target of CO
clusters were verified by measuring the angular distribution of the scattering light from the mixed gas target of CO (30%) and H
(30%) and H (70%). Moreover, the gas density profile was obtained by the interferometry. We will discuss the relation between gas density and a cluster size in the presentation.
(70%). Moreover, the gas density profile was obtained by the interferometry. We will discuss the relation between gas density and a cluster size in the presentation.
 , n) reactions in the laser-driven ion accelerator
, n) reactions in the laser-driven ion acceleratorSakaki, Hironao; Fukuda, Yuji; Kanasaki, Masato; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Jinno, Satoshi; Yogo, Akifumi; Fukami, Tomoyo; Watanabe, Yukinobu; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*
no journal, ,
In current researches, electron energies are getting higher as the high-energy ions are generated. Therefore, when the energy of ion exceeds several-tens of MeV, it is impossible to disregard the neutron generation from the ( , n) reactions. Although such a neutron becomes as a background-nose of the ion measurement, a quantitative evaluation has not carried out in the laser-driven ions acceleration experiments yet. We report an evaluation of those neutron properties by using measurement data in the laser-plasma interaction experiments, and it is discussed with a result of Monte Carlo simulation including the (
, n) reactions. Although such a neutron becomes as a background-nose of the ion measurement, a quantitative evaluation has not carried out in the laser-driven ions acceleration experiments yet. We report an evaluation of those neutron properties by using measurement data in the laser-plasma interaction experiments, and it is discussed with a result of Monte Carlo simulation including the ( , n) reaction processes.
, n) reaction processes.
 -rays
-raysHayakawa, Takehito
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hasegawa, Noboru; Nishikino, Masaharu; Yamagiwa, Mitsuru; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Suemoto, Toru; Tomita, Takuro*; Takei, Ryota*; Baba, Motoyoshi*
no journal, ,
The dynamical processes of the laser-induced surface modifications such as laser ablation come to attract much attention for the micro processing by the ultra-short laser pulse. The soft X-ray laser (SXRL) is suitable for probing the initial process of the surface morphological changes, because it has the suitable wavelength (= 13.9 nm, penetration depth = 5 nm), short duration (= 7 ps) and large photon numbers (larger than 1e+10 photons/shot). In this study, we have developed the femto-second laser pump and soft X-ray laser probe system with the soft X-ray interferometer in order to observe the dynamical processes of the femto-second laser ablation. By using this system, we measured the surface roughness and surface modifications of the laser induced metal surface. From this result, we succeeded to obtain the clear dependence for the material (Pt, Au, W) of the laser ablation dynamics.
Nishiuchi, Mamiko
no journal, ,
The proton beam attracts many potential fields of applications. This is because the laser-driven proton has many peculiar characteristics if compared with those of from the conventional accelerators. The report that the acceleration of the proton beam is successfully upto 120 MeV is reported with single shot base large laser system. The objective for us is to obtain the proton beam with energy more than 100 MeV with compact repetitive laser system. We have achieved 40 MeV proton beam with laser parameters of 8 J, 40 fs, contrast ratio of more than 10 and the peak intensity upto 10
and the peak intensity upto 10 Wcm
Wcm is focused onto the stainless steal tape target of 2 um. The energy conversion efficiency from laser to protons with energy more than 15 MeV is about 0.1%. We are now able to provide repetitive 40 MeV proton beam by more than 1Hz rep rate.
is focused onto the stainless steal tape target of 2 um. The energy conversion efficiency from laser to protons with energy more than 15 MeV is about 0.1%. We are now able to provide repetitive 40 MeV proton beam by more than 1Hz rep rate.